Table of Contents
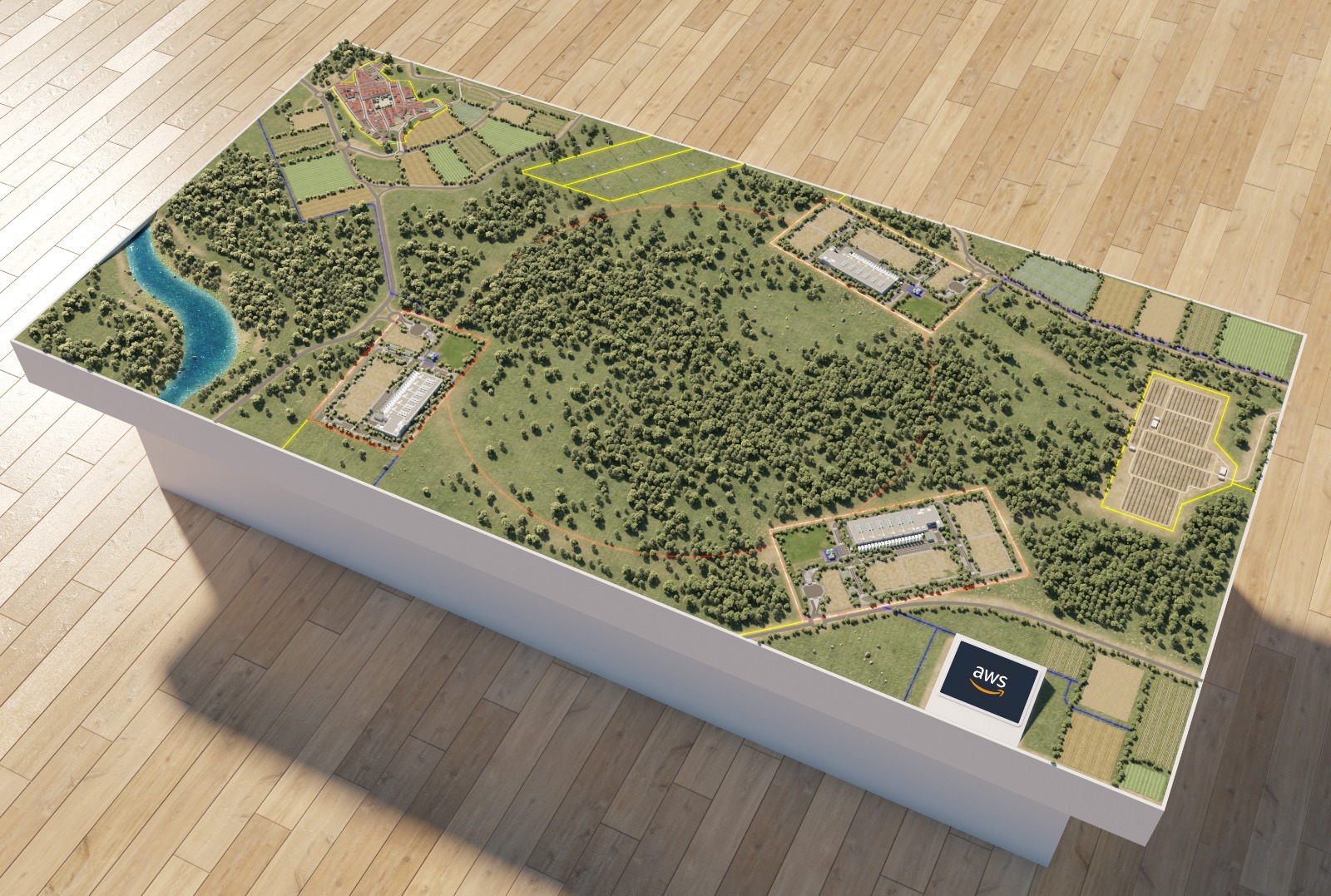
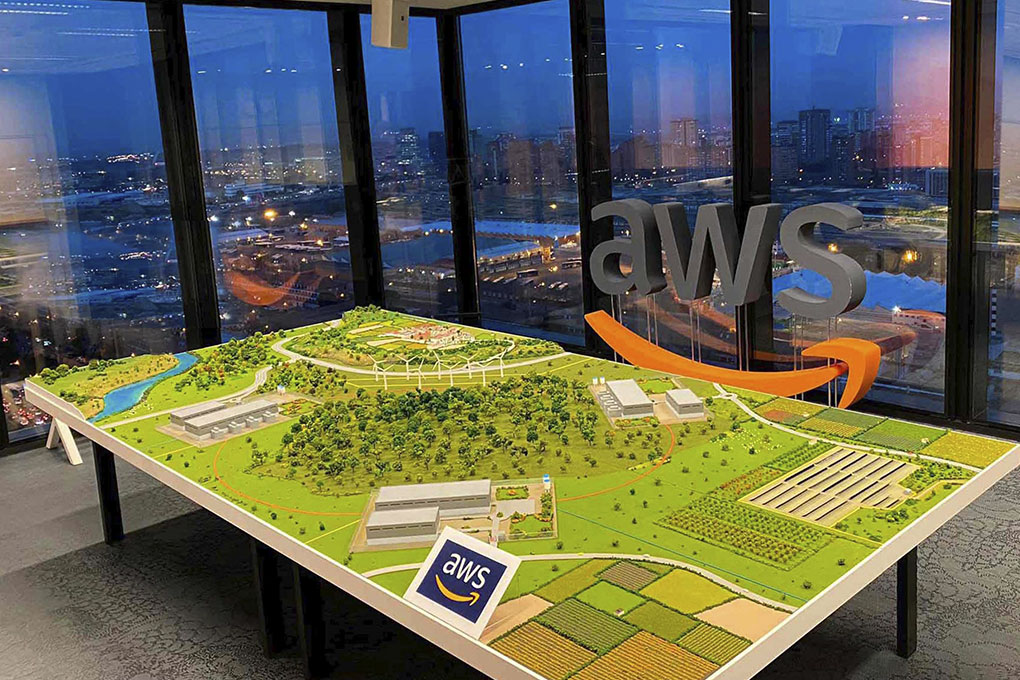
Landscape models, as their name suggests, are scaled representations of landscapes, typically symbolizing green areas that accompany buildings, generally through simple volumes.
One of the most important aspects of a model is to represent the surrounding space of the urban development or building where the project is to be carried out. This way, the nearby landscape areas or green zones are highlighted.
Keep reading!

What are landscape models?
As we have already mentioned, landscape models are scaled representations of the environment and existing elements, which, as a general rule, serve as a base for incorporating building models.
These are a kind of topographical model primarily used to describe the unique features of an environment. They are typically created at a large scale to clearly show topography, vegetation, ground cover, and other fine details.
How large are landscape models?
Given that landscape models represent broader terrains, the construction scale varies greatly depending on the extent of the terrain to be depicted, ranging from 1:50 to 1:2500. In landscape models, relief is very important, as this type of model can be said to be a three-dimensional map. Terrain elevations, as well as roads and urban and green zones, are the components of these prototypes.
What are landscape models used for?
Landscape models are very useful for studying a terrain intended for construction:
- The type of soil is analyzed.
- How a building would affect the surroundings.
- What problems might be encountered in the construction process.

How are landscape models made?
At Maquetas Tech, we draw on extensive expertise in crafting landscape models and fully understand how challenging the process can be: it demands solid topographical knowledge and the precise application of multiple scales.
To give you a general idea about the process, we explain some points below:
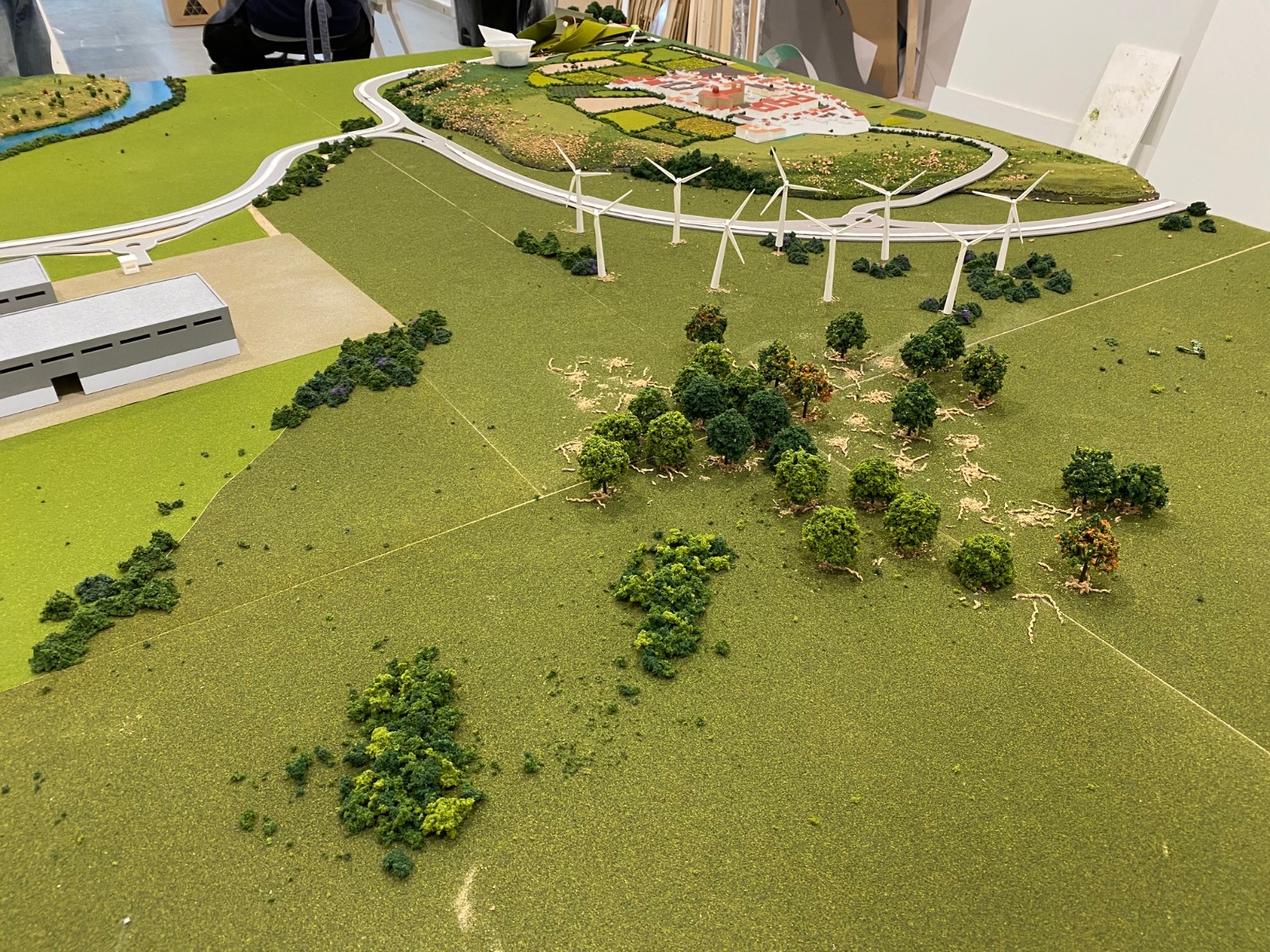
Selection of necessary materials
The materials usually depend on the final finish desired and the landscape to be represented. The most commonly used materials are cardboard (the most basic), followed by wood or cork.
The main element of this type of model is the topographical plan, which must include contour lines and these must be clearly marked. A trick is to print the plan on paper at actual size to be able to trace the base.
Cutting the materials
In the first step, we extracted the base of the model from the curve with the largest surface area. Next, we extract the other levels and superimpose them in the correct order, with the aim of achieving the 3-dimensional plane.
Final finishes
For the landscape model to look much more realistic, it is most common to use plaster paste or plastic cement to cover the 3-dimensional structure. Once dry, the rest of the decorative elements are added to give it greater realism. Additionally, it can be painted and textures such as grass, trees, and vegetation remnants can be added.
We hope this article about landscape models has been helpful. If you have a project in mind, do not hesitate to contact us. Our model makers will answer any questions you have.